ANIMAL HEALTH DEVELOPMENT
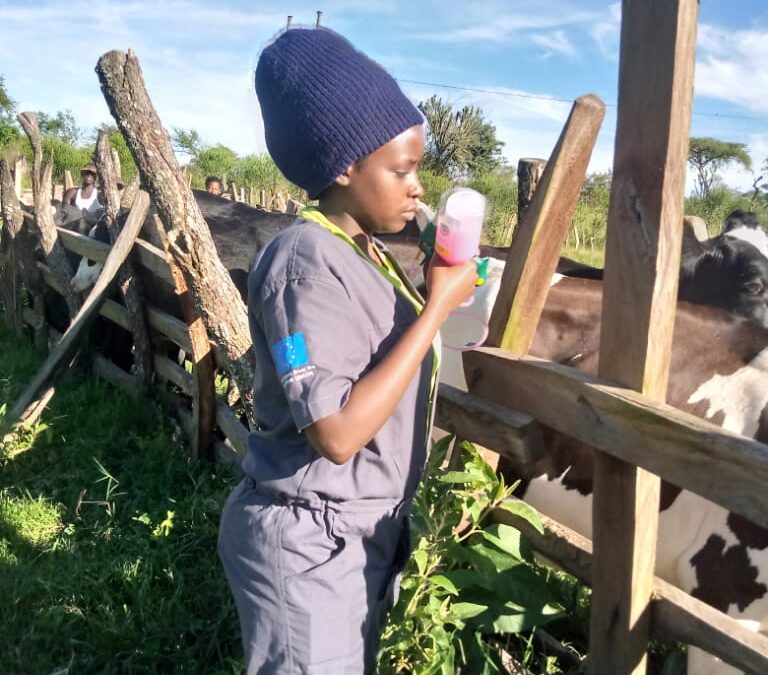
Animal health is an important aspect in the improvement of nutrition and livelihoods. This is one of the areas supported by the European Union (E.U) under the Farmer-Led Beef Livestock Investment and Sustainability project (FALBIIS), implemented by Uganda Meat Producers Cooperative Union Ltd. This involves ensuring the aspects below are considered:
1. Livestock Disease Surveillance and Monitoring
There are endemic diseases affecting animals periodically, so there is a need to monitor and check for indicators leading to this. Routine examinations are also done during such visits and reports sought from the farms or veterinary counterparts.
2. Livestock Disease Outbreak Investigation using laboratory diagnosis of animal specimen samples. For instance, where there is a rampant abortion of animals or a particular disease outbreak, the UMPCU veterinary doctor goes to the farm and picks samples (blood or faecal), for further analysis and disease diagnostics.
3. Animal Disease Case Management and/or Treatment e.g. Tick-Borne diseases, fevers, diarrhea, etc. Once the diagnosis has been made then the case is managed, and the sick animals are immediately attended to.
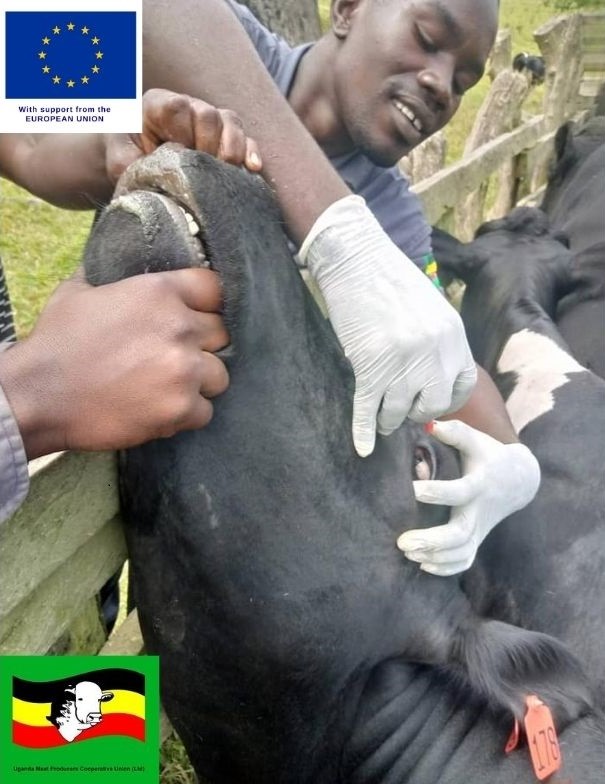
4. Livestock Disease Prevention and Control through vaccination for all notifiable diseases like Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD), Contagious Bovine Pleuro-Pneumonia (CBPP), and Clostridial infections among others. Animals that are susceptible to disease infection are either vaccinated or managed appropriately.
5. Strategic control of parasitic diseases such as deworming using anti-helminthic (dewormers). Usually, during the rainy season, it is advisable to treat the cattle which are susceptible to worms infestation and need to be controlled. In the case of tick control, intervals of treatment using acaricides are moderated accordingly.
6. Emergency and Corrective surgical operations like calf-delivery by Cesarean section (C-section) etc. For example, if an animal has eaten something which causes bloating, or is injured, or suspected to have swallowed a sharp object, it is attended to with such procedures.
Source of information: Dr. Joseph Ruhinda, Programs Manager

